- ABOUT GSI
- ABOUT GSI
-
-
-
High Performance, High Reliability, Low Power
- CORPORATE PROFILE
- GSI PATENTS
- QUALITY INFORMATION, REPORTS, AND CERTIFICATIONS
- MARKS AND STYLE GUIDELINES
- Academic Papers
-
-
-
-
- SALES
- INVESTOR RELATIONS
- ABOUT GSI
- SEARCH
- OVERVIEW
-
-
-
The cornerstone of similarity search
- Search Overview
-
-
-
-
- VECTOR SEARCH
-
-
-
Data to Knowledge to Insight to Action
- VECTOR SEARCH Overview
-
-
-
-
- MOLECULAR SEARCH
-
-
-
Technology that benefits human health
- Molecular Search Overview
-
-
-
-
- FACIAL RECOGNITION
-
-
-
Safety and Security
- Facial Recognition Overview
-
-
-
-
- SAAS
-
-
-
Hosted services for GSI APU applications
- SaaS OVERVIEW
-
-
-
-
- OVERVIEW
- HPC
- OVERVIEW
-
-
-
High performance compute-in-memory
- HPC Overview
-
-
-
-
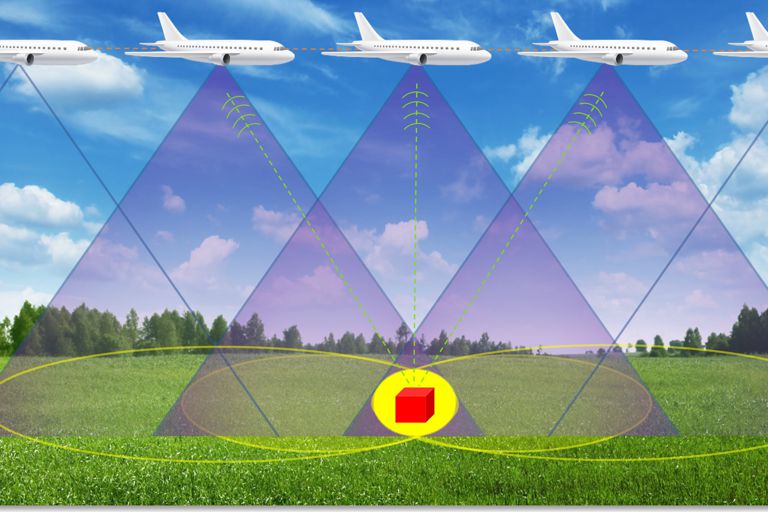
- SYNTHETIC APERTURE RADAR
-
-
-
Bringing real-time datacenter SAR processing to mobile applications
- SAR Overview
-
-
-
-
- GPS-DENIED NAVIGATION
-
-
-
Next Gen Navigation
- GPS-Denied Navigation Overview
-
-
-
-
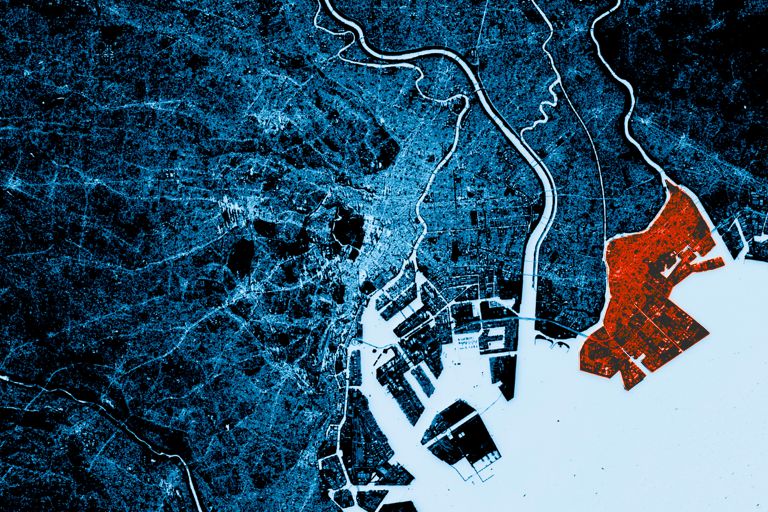
- CHANGE DETECTION
-
-
-
Can’t hide from the APU
- Change Detection Overview
-
-
-
-
- OVERVIEW
- GENERATIVE AI
- GENERATIVE AI
-
-
-
Personalized, relevant search through natural language
- Generative AI Overview
-
-
-
-
- GENERATIVE AI
- AEROSPACE & DEFENSE
- OVERVIEW
-
-
-
Efficiently processing big data for A&D applications
- Aerospace & Defense Overview
- Aerospace & Defense Brochure
-
-
-
-
- SYNTHETIC APERTURE RADAR
-
-
-
Bringing real-time datacenter SAR processing to mobile applications
- SAR Overview
-
-
-
-
- OBJECT RECOGNITION
-
-
-
APU finds the needle in the haystack
- Object Recognition Overview
-
-
-
-
- GPS-DENIED ENVIRONMENT
-
-
-
Next Gen Navigation
- GPS-Denied Environment Overview
-
-
-
-
- DATA FUSION
-
-
-
Advanced threat detection
- Data Fusion Overview
-
-
-
-
- RADIATION-HARDENED SRAMs
-
-
-
From stringent space-grade memory to AI acceleration
- Radiation-Hardened SRAMs
-
-
-
-
- RADIATION-TOLERANT SRAMs
-
-
-
From stringent space-grade memory to AI acceleration
- Radiation-Tolerant SRAMs
-
-
-
-
- OVERVIEW
- MEMORY
- MEMORY
-
-
-
The highest performance, highest density monolithic SRAMs
- OVERVIEW
- Quad SRAMs
- DDR SRAMs
- NBT SRAMs
- SyncBurst SRAMs
- Asynchronous SRAMs
- Low Latency DRAMs
- IP Ports
-
-
-
-
- RADIATION-HARDENED SRAMs
-
-
-
From stringent space-grade memory to AI acceleration
- Radiation-Hardened SRAMs
-
-
-
-
- RADIATION-TOLERANT SRAMs
-
-
-
From stringent space-grade memory to AI acceleration
- Radiation-Tolerant SRAMs
-
-
-
-
- PARAMETRIC SEARCH
- CROSS REFERENCE SEARCH
- MEMORY BROCHURE
- REFERENCE LIBRARY
- MEMORY
- RESOURCES
- INDEPTH
-
-
-
Visionary thought leadership
- Blog Listings
- Whitepapers
- Podcasts
- Academic Papers
-
-
-
- TOOLS
-
-
-
Create, maintain, debug
- Tools Overview
-
-
-
-
- INDEPTH